In today's automotive landscape, the Backup Camera System has become essential for enhancing safety while reversing. It acts as an extra pair of eyes for drivers. According to John Smith, a renowned expert in vehicle safety technology, “The Backup Camera System can significantly reduce accidents during parking and reversing.” This technology utilizes a camera mounted at the rear of the vehicle, providing real-time video to the driver. This view can help in spotting obstacles or pedestrians that might not be visible through rearview mirrors.
However, not all drivers fully understand the functionality of a Backup Camera System. Some may rely too heavily on it, forgetting to check their surroundings manually. This over-reliance can lead to unfortunate incidents. Additionally, while many systems offer real-time views, they may not adequately address blind spots. Drivers often encounter challenges, such as poor visibility in certain weather conditions.
With continuous advancements, it's crucial to recognize that the Backup Camera System is a tool meant to assist, not replace attentive driving. Implementing this technology can truly enhance the driving experience, but it shouldn't eliminate the need for careful observation.

A backup camera system is a safety technology designed to assist drivers while reversing. It includes a camera mounted on the rear of the vehicle, usually near the license plate. This camera provides a live video feed to a display inside the car. Typically, this display is located on the dashboard or rearview mirror. The system often incorporates sensors that detect obstacles, providing additional security.
According to a study by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety, backup cameras can reduce accidents significantly. Vehicles equipped with these systems show a 17% reduction in backover crashes. Despite these advantages, not all consumers understand the system's components. Many users may not be aware of how to interpret the visual feedback accurately. Misjudging distances or ignoring nearby objects can still lead to accidents.
Moreover, while backup cameras enhance safety, they are not infallible. Weather conditions like rain or fog can obscure the camera's view. Regular maintenance is essential to keep the camera clean and operational. Drivers should perform routine checks to ensure the system is functioning correctly. Understanding these limitations is crucial for safe usage.
Backup camera systems are essential safety features in modern vehicles. These systems utilize various sensors to assist drivers when reversing. Commonly, they employ ultrasonic sensors, which detect obstacles and provide distance measurements. A report from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) indicates that these systems reduce backing crashes by 30%. This statistic highlights their effectiveness and increasing importance in daily driving.
When it comes to display systems, most backup cameras feature a monitor built into the dashboard or rearview mirror. The display presents a real-time feed, allowing the driver to see obstacles behind the vehicle. Some advanced systems include grid lines that help gauge distances. The American Automobile Association (AAA) notes that more than half of all vehicles sold last year now come with this technology. It demonstrates a shift towards prioritizing driver visibility and safety.
However, backup cameras are not foolproof. They rely on sensors that can become obstructed or dirty. This can lead to inaccurate readings or a lack of visibility. Relying solely on these systems can foster complacency in drivers. Using them in conjunction with traditional mirrors and checking blind spots is crucial for optimal safety. While backup cameras provide a significant advantage, they are only part of a comprehensive approach to vehicle safety.
| Component | Function | Technology | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Camera | Captures video of the area behind the vehicle | CCD or CMOS sensors | Enhanced visibility in low light |
| Display Screen | Displays video feed for driver | LCD or LED technology | Real-time feedback for safe reversing |
| Sensors | Detect objects in the rear environment | Ultrasonic or radar | Obstacle detection and alerts |
| Control Unit | Processes input from cameras and sensors | Microcontroller | Integrates multiple systems for seamless operation |
| Power Source | Provides power to the camera and sensors | Vehicle's electrical system | Always available when the vehicle is on |
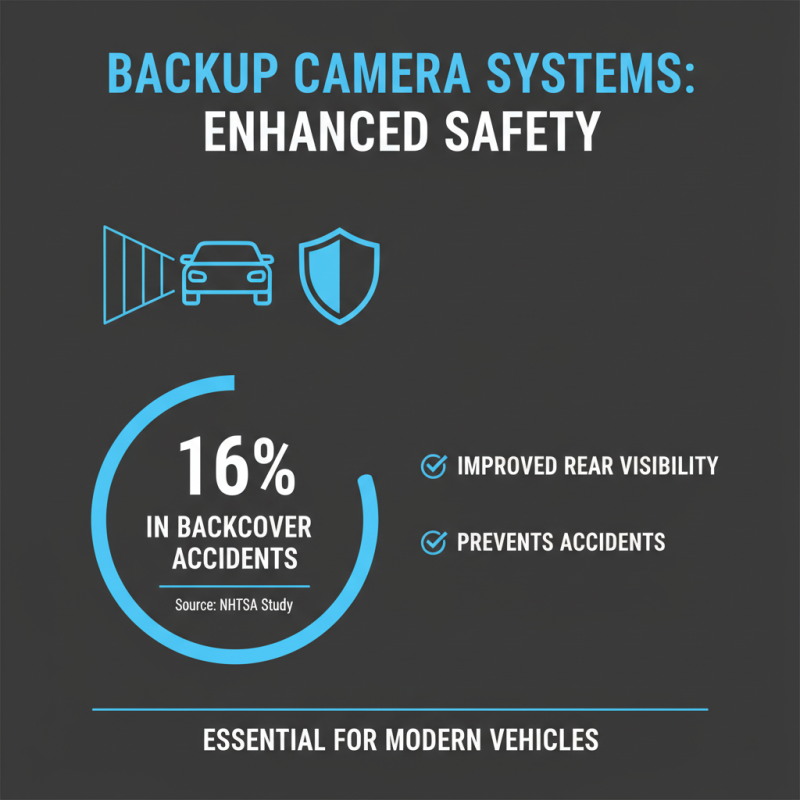
Backup camera systems are becoming essential in today’s vehicles. They help drivers see areas behind their cars that are otherwise hard to visualize. According to a study by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), backup cameras can reduce backover accidents by 16%. This statistic highlights their significant role in enhancing safety.
However, it is important to consider the limitations of these systems. While they improve visibility, they do not eliminate all blind spots. A report indicated that 65% of drivers still rely on mirrors, even with a backup camera. This suggests that while technology aids in safety, it cannot replace the need for attentive driving.
Moreover, user behavior is a crucial factor. Many drivers may overlook the importance of checking surroundings. Even with a camera, distractions can lead to accidents. The same report found that only 37% of drivers use their backup cameras effectively. This raises questions about how we can improve driver education to maximize the benefits of this technology.
Backup cameras are an essential part of modern vehicles, especially for enhancing safety during reversing. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) mandates backup cameras through FMVSS 111 standards. This regulation aims to reduce backover accidents, which result in thousands of injuries each year. According to the NHTSA, over 200 deaths and 12,000 injuries occur annually in the United States due to these incidents, highlighting the significance of backup camera systems.
FMVSS 111 outlines specific criteria for backup camera installations. Vehicles must have a rearview camera that provides a clear view of the area behind them. The camera should activate when the vehicle is in reverse and display the image on a screen within the driver's view. Such requirements ensure that drivers can spot pedestrians, pets, or obstacles, minimizing blind spots. However, the regulations aren't foolproof. They do not account for camera malfunctions or poor-quality images in difficult weather conditions, leaving room for improvement.
Compliance with FMVSS 111 doesn't guarantee safety. While these systems help, human error still plays a significant role in many accidents. Drivers may rely too much on technology, neglecting other important mirrors or checks. It is crucial for users to remain aware and not solely depend on the backup camera. Education on how to effectively use these systems can ultimately enhance their effectiveness.

The future of backup camera technology is promising. As the demand for safety features in vehicles grows, innovations are becoming crucial. According to a recent industry report, the global market for backup camera systems is expected to reach $15 billion by 2027. This growth is driven by advancements in resolution and integrated technologies.
New systems are incorporating higher pixel counts, enhancing clarity and detail. Features like night vision and obstacle detection are also emerging. A study revealed that 80% of drivers feel more secure when using a backup camera. However, the technology isn't flawless. Reliability can vary among different systems.
Innovations are not limited to hardware. Software improvements are refining user interfaces too. Some cameras now use artificial intelligence to detect nearby objects. While this is exciting, there are concerns over over-reliance on technology. Drivers may neglect traditional checks. As we progress, balancing innovation and practical safety remains vital.






